Jump to page sections
This is a sample PowerShell script for getting some info about hardware, BIOS, OS and network configuration on a target computer. Adapt as necessary. This is well-suited for being placed on a terminal server for use by IT personnel / the help desk. If you do not enter any parameters, such as when launching it from a GUI/shortcut, you will be prompted for a computer name.'''NB!''' This article is old, one of the first I wrote, and the style of the code in some parts is not something you should be learning from, but as a side-effect of me learning as I was going, there is quite a bit of comments. The primary thing I would like to mention is that "$Private:VariableNameHere" should be replaced by simply "$VariableNameHere" where the variables are made private in the script.
You can however look at the various WMI classes in the code and the techniques for collecting data from them. Adding this comment is me not doing the right thing and rewriting this article entirely... Sorry.Use the switch parameter ''-IgnorePing'' to attempt to gather data even if you do not get an ICMP ping reply.
It requires Quest ActiveRoles cmdlets for full functionality, but will simply skip that part, with a "warning", if you don't have it. Quest requires .NET 3.5 SP1 or higher, as does the Out-GridView cmdlet used for GUI output at the end.NB! Quest is now dead in the water since this article and script were written, and hasn't been updated since 2013, and the latest free version from quest.com is on that page I link to above now (and no longer on quest.com). Most people are better off looking at Get-ADComputer and Get-ADUser from the Microsoft cmdlets now, in a Server 2008 R2 environment and up. For 2003 R2 DCs (there shouldn't be any, though), Quest is still probably the best choice.
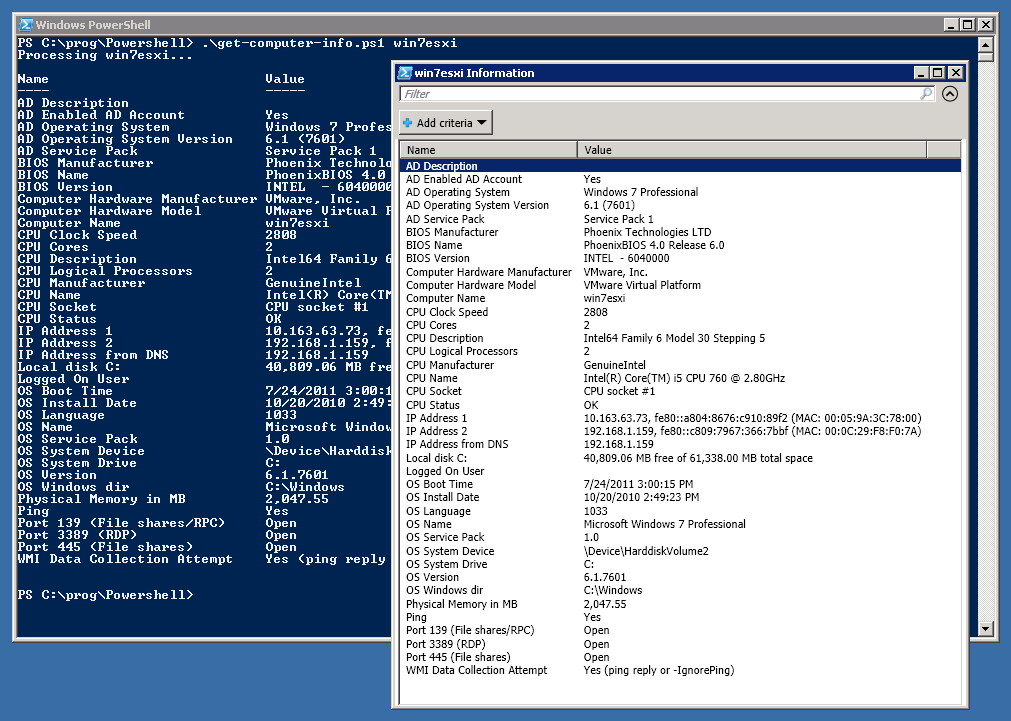
It will retrieve BIOS information about hardware, CPU information, memory/RAM, open ports using sockets (also see my module/script for checking for open TCP ports), AD account status and info, available disk space on local drives, IP address(es) on all network interfaces, MAC address(es), OS version, OS service pack, find the logged on user. Finding the logged on user this way is not 100% reliable in my experience, nor is psloggedon.exe from PSTools (I think this comment is redundant after a certain PsLoggedOn.exe version where it works - I wrote an article about that here years after writing this one). The Win32::NetAdmin or Win32::AdminMisc Perl modules and PsLoggedOn.exe would seemingly sometimes only report users logged on to the console, not via RDP.Terminal Server Use
Example Screenshot
PS C:\Powershell> .\get-computer-info.ps1 corpcomp1 -IgnorePing
Download
Download Get-Computer-Info.ps1 (right-click and "save as").
Code
param(
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)] $TargetComputer,
[switch] $IgnorePing
)
# Check that the Quest.ActiveRoles.ADManagement snapin is available
# If not, just print a warning rather than exiting as is usually necessary.
if (!(Get-PSSnapin Quest.ActiveRoles.ADManagement -registered -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue)) {
'You need the Quest ActiveRoles AD Management Powershell snapin to fully use this script'
"www.quest.com`n"
'Please install and register this snapin.'
}
# Add the snapin and don't display an error if it's already added.
# If it's not registered, the warning above will be printed, but
# I changed it from exiting, as I normally have it do, to just continuing,
# because WMI, DNS, etc. might still work.
Add-PSSnapin Quest.ActiveRoles.ADManagement -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
$private:computer = $targetComputer
'Processing ' + $private:computer + '...'
# Declare main data hash to be populated later
$data = @{}
$data.'Computer Name' = $private:computer
# Try an ICMP ping the only way Powershell knows how...
$private:ping = Test-Connection -quiet -count 1 $private:computer
$data.Ping = $(if ($private:ping) { 'Yes' } else { 'No' })
# Do a DNS lookup with a .NET class method. Suppress error messages.
$ErrorActionPreference = 'SilentlyContinue'
if ( $private:ips = [System.Net.Dns]::GetHostAddresses($private:computer) | foreach { $_.IPAddressToString } ) {
$data.'IP Address(es) from DNS' = ($private:ips -join ', ')
}
else {
$data.'IP Address from DNS' = 'Could not resolve'
}
# Make errors visible again
$ErrorActionPreference = 'Continue'
# We'll assume no ping reply means it's dead. Try this anyway if -IgnorePing is specified
if ($private:ping -or $private:ignorePing) {
$data.'WMI Data Collection Attempt' = 'Yes (ping reply or -IgnorePing)'
# Get various info from the ComputerSystem WMI class
if ($private:wmi = Get-WmiObject -Computer $private:computer -Class Win32_ComputerSystem -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue) {
$data.'Computer Hardware Manufacturer' = $private:wmi.Manufacturer
$data.'Computer Hardware Model' = $private:wmi.Model
$data.'Physical Memory in MB' = ($private:wmi.TotalPhysicalMemory/1MB).ToString('N')
$data.'Logged On User' = $private:wmi.Username
}
$private:wmi = $null
# Get the free/total disk space from local disks (DriveType 3)
if ($private:wmi = Get-WmiObject -Computer $private:computer -Class Win32_LogicalDisk -Filter 'DriveType=3' -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue) {
$private:wmi | Select 'DeviceID', 'Size', 'FreeSpace' | Foreach {
$data."Local disk $($_.DeviceID)" = ('' + ($_.FreeSpace/1MB).ToString('N') + ' MB free of ' + ($_.Size/1MB).ToString('N') + ' MB total space' )
}
}
$private:wmi = $null
# Get IP addresses from all local network adapters through WMI
if ($private:wmi = Get-WmiObject -Computer $private:computer -Class Win32_NetworkAdapterConfiguration -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue) {
$private:Ips = @{}
$private:wmi | Where { $_.IPAddress -match '\S+' } | Foreach { $private:Ips.$($_.IPAddress -join ', ') = $_.MACAddress }
$private:counter = 0
$private:Ips.GetEnumerator() | Foreach {
$private:counter++; $data."IP Address $private:counter" = '' + $_.Name + ' (MAC: ' + $_.Value + ')'
}
}
$private:wmi = $null
# Get CPU information with WMI
if ($private:wmi = Get-WmiObject -Computer $private:computer -Class Win32_Processor -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue) {
$private:wmi | Foreach {
$private:maxClockSpeed = $_.MaxClockSpeed
$private:numberOfCores += $_.NumberOfCores
$private:description = $_.Description
$private:numberOfLogProc += $_.NumberOfLogicalProcessors
$private:socketDesignation = $_.SocketDesignation
$private:status = $_.Status
$private:manufacturer = $_.Manufacturer
$private:name = $_.Name
}
$data.'CPU Clock Speed' = $private:maxClockSpeed
$data.'CPU Cores' = $private:numberOfCores
$data.'CPU Description' = $private:description
$data.'CPU Logical Processors' = $private:numberOfLogProc
$data.'CPU Socket' = $private:socketDesignation
$data.'CPU Status' = $private:status
$data.'CPU Manufacturer' = $private:manufacturer
$data.'CPU Name' = $private:name -replace '\s+', ' '
}
$private:wmi = $null
# Get BIOS info from WMI
if ($private:wmi = Get-WmiObject -Computer $private:computer -Class Win32_Bios -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue) {
$data.'BIOS Manufacturer' = $private:wmi.Manufacturer
$data.'BIOS Name' = $private:wmi.Name
$data.'BIOS Version' = $private:wmi.Version
}
$private:wmi = $null
# Get operating system info from WMI
if ($private:wmi = Get-WmiObject -Computer $private:computer -Class Win32_OperatingSystem -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue) {
$data.'OS Boot Time' = $private:wmi.ConvertToDateTime($private:wmi.LastBootUpTime)
$data.'OS System Drive' = $private:wmi.SystemDrive
$data.'OS System Device' = $private:wmi.SystemDevice
$data.'OS Language ' = $private:wmi.OSLanguage
$data.'OS Version' = $private:wmi.Version
$data.'OS Windows dir' = $private:wmi.WindowsDirectory
$data.'OS Name' = $private:wmi.Caption
$data.'OS Install Date' = $private:wmi.ConvertToDateTime($private:wmi.InstallDate)
$data.'OS Service Pack' = [string]$private:wmi.ServicePackMajorVersion + '.' + $private:wmi.ServicePackMinorVersion
}
# Scan for open ports
$ports = @{
'File shares/RPC' = '139' ;
'File shares' = '445' ;
'RDP' = '3389';
#'Zenworks' = '1761';
}
foreach ($service in $ports.Keys) {
$private:socket = New-Object Net.Sockets.TcpClient
# Suppress error messages
$ErrorActionPreference = 'SilentlyContinue'
# Try to connect
$private:socket.Connect($private:computer, $ports.$service)
# Make error messages visible again
$ErrorActionPreference = 'Continue'
if ($private:socket.Connected) {
$data."Port $($ports.$service) ($service)" = 'Open'
$private:socket.Close()
}
else {
$data."Port $($ports.$service) ($service)" = 'Closed or filtered'
}
$private:socket = $null
}
}
else {
$data.'WMI Data Collected' = 'No (no ping reply and -IgnorePing not specified)'
}
# Get data from AD using Quest ActiveRoles Get-QADComputer
$private:computerObject = Get-QADComputer $private:computer -ErrorAction 'SilentlyContinue'
if ($private:computerObject) {
$data.'AD Operating System' = $private:computerObject.OSName
$data.'AD Operating System Version' = $private:computerObject.OSVersion
$data.'AD Service Pack' = $private:computerObject.OSServicePack
$data.'AD Enabled AD Account' = $( if ($private:computerObject.AccountIsDisabled) { 'No' } else { 'Yes' } )
$data.'AD Description' = $private:computerObject.Description
}
else {
$data.'AD Computer Object Info Collected' = 'No'
}
# Output data
$data.GetEnumerator() | Sort-Object 'Name' | Format-Table -AutoSize
$data.GetEnumerator() | Sort-Object 'Name' | Out-GridView -Title "$private:computer Information"
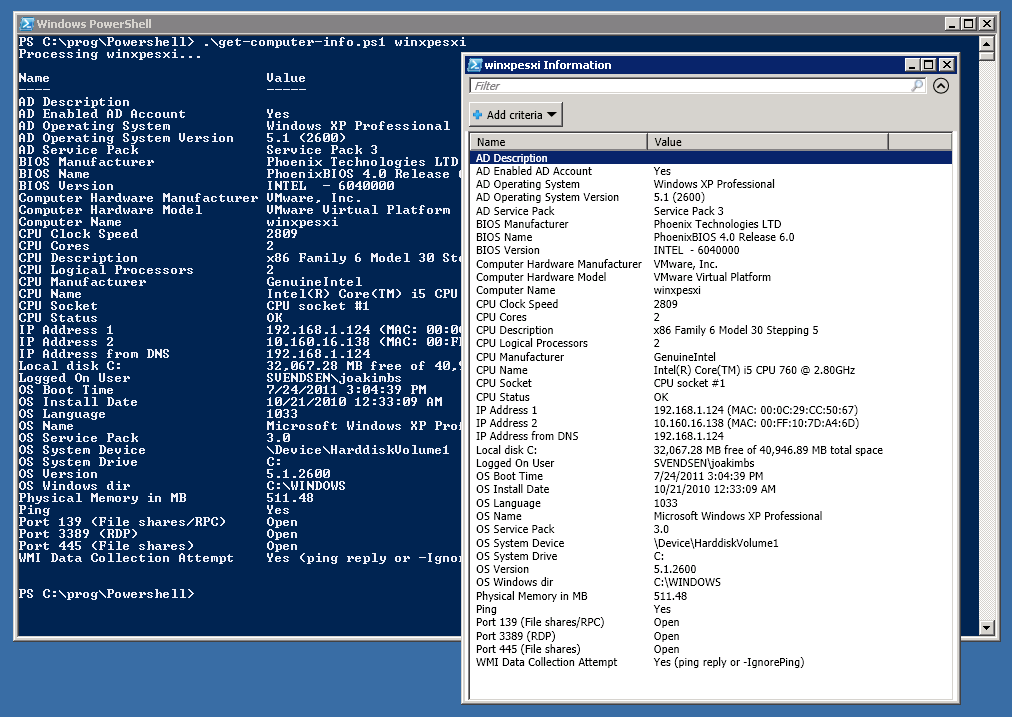
Example Screenshot 2
 Powershell
Windows
Powershell
Windows
Blog articles in alphabetical order
A
- A Look at the KLP AksjeNorden Index Mutual Fund
- A primitive hex version of the seq gnu utility, written in perl
- Accessing the Bing Search API v5 using PowerShell
- Accessing the Google Custom Search API using PowerShell
- Active directory password expiration notification
- Aksje-, fonds- og ETF-utbytterapportgenerator for Nordnet-transaksjonslogg
- Ascii art characters powershell script
- Automatically delete old IIS logs with PowerShell
C
- Calculate and enumerate subnets with PSipcalc
- Calculate the trend for financial products based on close rates
- Check for open TCP ports using PowerShell
- Check if an AD user exists with Get-ADUser
- Check when servers were last patched with Windows Update via COM or WSUS
- Compiling or packaging an executable from perl code on windows
- Convert between Windows and Unix epoch with Python and Perl
- Convert file encoding using linux and iconv
- Convert from most encodings to utf8 with powershell
- ConvertTo-Json for PowerShell version 2
- Create cryptographically secure and pseudorandom data with PowerShell
- Crypto is here - and it is not going away
- Crypto logo analysis ftw
D
G
- Get rid of Psychology in the Stock Markets
- Get Folder Size with PowerShell, Blazingly Fast
- Get Linux disk space report in PowerShell
- Get-Weather cmdlet for PowerShell, using the OpenWeatherMap API
- Get-wmiobject wrapper
- Getting computer information using powershell
- Getting computer models in a domain using Powershell
- Getting computer names from AD using Powershell
- Getting usernames from active directory with powershell
- Gnu seq on steroids with hex support and descending ranges
- Gullpriser hos Gullbanken mot spotprisen til gull
H
- Have PowerShell trigger an action when CPU or memory usage reaches certain values
- Historical view of the SnP 500 Index since 1927, when corona is rampant in mid-March 2020
- How Many Bitcoins (BTC) Are Lost
- How many people own 1 full BTC
- How to check perl module version
- How to list all AD computer object properties
- Hva det innebærer at særkravet for lån til sekundærbolig bortfaller
I
L
M
P
- Parse openssl certificate date output into .NET DateTime objects
- Parse PsLoggedOn.exe Output with PowerShell
- Parse schtasks.exe Output with PowerShell
- Perl on windows
- Port scan subnets with PSnmap for PowerShell
- PowerShell Relative Strength Index (RSI) Calculator
- PowerShell .NET regex to validate IPv6 address (RFC-compliant)
- PowerShell benchmarking module built around Measure-Command
- Powershell change the wmi timeout value
- PowerShell check if file exists
- Powershell check if folder exists
- PowerShell Cmdlet for Splitting an Array
- PowerShell Executables File System Locations
- PowerShell foreach loops and ForEach-Object
- PowerShell Get-MountPointData Cmdlet
- PowerShell Java Auto-Update Script
- Powershell multi-line comments
- Powershell prompt for password convert securestring to plain text
- Powershell psexec wrapper
- PowerShell regex to accurately match IPv4 address (0-255 only)
- Powershell regular expressions
- Powershell split operator
- Powershell vs perl at text processing
- PS2CMD - embed PowerShell code in a batch file
R
- Recursively Remove Empty Folders, using PowerShell
- Remote control mom via PowerShell and TeamViewer
- Remove empty elements from an array in PowerShell
- Remove first or last n characters from a string in PowerShell
- Rename unix utility - windows port
- Renaming files using PowerShell
- Running perl one-liners and scripts from powershell
S
- Sammenlign gullpriser og sølvpriser hos norske forhandlere av edelmetall
- Self-contained batch file with perl code
- Silver - The Underrated Investment
- Simple Morningstar Fund Report Script
- Sølv - den undervurderte investeringen
- Sort a list of computers by domain first and then name, using PowerShell
- Sort strings with numbers more humanely in PowerShell
- Sorting in ascending and descending order simultaneously in PowerShell
- Spar en slant med en optimalisert kredittkortportefølje
- Spre finansiell risiko på en skattesmart måte med flere Aksjesparekontoer
- SSH from PowerShell using the SSH.NET library
- SSH-Sessions Add-on with SCP SFTP Support
- Static Mutual Fund Portfolio the Last 2 Years Up 43 Percent
- STOXR - Currency Conversion Software - Open Exchange Rates API
