Jump to page sections
- Proof of Concept
- Module Functions
- New-SshSession
- New-SshSession Help Text
- New-SshSession Example
- Invoke-SshCommand
- Invoke-SshCommand Help Text
- Invoke-SshCommand Example
- Get-SshSession
- Get-SshSession Help Text
- Get-SshSession Example
- Enter-SshSession
- Enter-SshSession Help Text
- Enter-SshSession Example
- Remove-SshSession
- Remove-SshSession Help Text
- Remove-SshSession Example
- SCP Add-on Feature
- Experimental sudo Support
- Downloads
- The PowerShell gallery version
- Demo of pipeline support
- A Few Quick Tips About How To Use The Module
- A Few Notes About Creating a Key for ESXi 5.x
For various reasons you might want to execute commands via SSH, using PowerShell. Presented here is a module with functions (that work like cmdlets or commands) for running commands via SSH on remote hosts such as Linux or Unix computers, VMware ESX(i) hosts or network equipment such as routers and switches that support SSH. It seems to work very well against OpenSSH-type servers.
The module uses the SSH.NET library which you can find on GitHub (formerly on CodePlex). Also see the downloads section below where I've bundled the DLLs I've tested with.Starting with the good news about VMware: ESX(i) 4.x seems to be supported.
However, I've found that when I try to connect to VMware ESXi 5.x using this module/library, using a password, I get the error "Unable to connect to 192.168.1.103: Exception calling "Connect" with "0" argument(s): "No suitable authentication method found to complete authentication."". So it appears the authentication method ESXi implements isn't supported by the SSH.NET library, or maybe the other way around... The developers suggest an approach to handle "No suitable authentication method found to complete authentication" here (dead link now...). I have tested this, but I'm getting an unexpected error related to the event handler.The code I'm using and error I'm getting is what the poster "Jaykul" describes somewhere near the bottom of this thread.
Using a key will, however, work. See the bottom of this article for more information on that. Given that, I suppose using this module to add keys to hosts running 4.x might be a good idea before upgrading them to 5.x to avoid manual labour (except the keys seem to be cleared on upgrade?).The majority of this was written in a couple of days and must be considered beta - but as of November 2017 this module has been downloaded over 80,000 times, and I've not heard much about bugs beyond wanting to be able to use key files in the current directory without using a full path (this is now supported in the "SCP add-on version"). I've realized a few design decisions were quite poor, but rewriting seems daunting. This project is now also on GitHub in the PowerShell gallery version (the best one, it supports PScredentials objects, etc.).
2021-10-29: I have not used this module myself in years. This page was moved from MediaWiki to mostly static HTML. There can be formatting bugs and internal link bugs as a result of the reproduction. But the article gets a fair bit of traffic. The module is easily upgraded to a newer SSH.NET library by replacing the DLL (presumably, untested). Now that it's 2021, this module has been downloaded roughly half a million times, so I think some people depend on it... I feel guilty for not maintaining it better. Maybe there are meta blog posts about this blog post that describe how to use the module. Still no feedback, not even on GitHub, except for one issue I vaguely remember about including the word "error". I feel like a lonely cowboy... Currently, I interpret it as "it is of sufficient quality"?
I should also mention that importing private keys created with Putty will not work, as the Putty developer apparently uses a different key format standard than (most of) the rest of the world. The OpenSSH key format is currently supported, but the Putty key format might be supported later if the developers implement it. There's a thread about it in the discussion forums on their CodePlex page. Oh, and PuttyGen.exe can save/export keys in OpenSSH format if you tell it to.
Enjoy!Proof of Concept
Module Functions
By the way, thanks to Jonathan Medd for writing this nice article about how to use the module. There is now a -Credential parameter in the latest PowerShell gallery and GitHub version - and also a -KeyPass parameter as well as a -KeyCredential parameter.
To list the cmdlets to get help for from the command line, use something like this, after you've loaded the module:PS E:\> get-help *ssh* Name Category Synopsis ---- -------- -------- Get-SshSession Function Shows all, or the specified, SSH sessions in the global $SshSessions var... Remove-SshSession Function Removes opened SSH connections. Use the parameter -RemoveAll to remove a... New-SshSession Function Creates SSH sessions to remote SSH-compatible hosts, such as Linux... Invoke-SshCommand Function Invoke/run commands via SSH on target hosts to which you have already op... Enter-SshSession Function Enter a primitive interactive SSH session against a target host....
Or:
Get-Command -Module SSH-Sessions
Here is an article that demonstrates how to parse "df" output from the Linux side to produce custom PS objects containing the data, properly typed (numerical/string).
New-SshSession
The first thing you do when you want to interact with hosts via SSH using this module, is to create SSH sessions to the target host or hosts.
The global $SshSessions variable will be populated with SSH client objects from the SSH.NET library (Renci), but you do not normally need to access this for basic use.You can connect to multiple hosts at the same time using the same credentials, and to other hosts with other credentials by running the command again with different credentials. They will be added to the SSH client pool maintained in $SshSessions.
New-SshSession Help Text
<# .SYNOPSIS Creates SSH sessions to remote SSH-compatible hosts, such as Linux or Unix computers or network equipment. You can later issue commands to be executed on one or more of these hosts. .DESCRIPTION Once you've created a session, you can use Invoke-SshCommand or Enter-SshSession to send commands to the remote host or hosts. The authentication is done here. If you specify -KeyFile, that will be used. If you specify a password and no key, that will be used. If you do not specify a key nor a password, you will be prompted for a password, and you can enter it securely with asterisks displayed in place of the characters you type in. .PARAMETER ComputerName Required. DNS names or IP addresses for target hosts to establish a connection to using the provided username and key/password. .PARAMETER Username Required. The username used for connecting. .PARAMETER KeyFile Optional. Specify the path to a private key file for authenticating. Overrides a specified password. .PARAMETER Password Optional. You can specify a key, or leave out the password to be prompted for a password which is typed in interactively and will not be displayed. .PARAMETER Port Optional. Default 22. Target port the SSH server uses. #>
New-SshSession Example
PS E:\> New-SshSession -ComputerName ubuntu64esxi,192.168.1.153 -Username joakimbs No key provided. Enter SSH password for joakimbs: **************** Successfully connected to ubuntu64esxi Successfully connected to 192.168.1.153 # This global variable is set by the module and contains the sessions. # But you normally use the cmdlet Get-SshSessions to inspect. PS E:\> $SshSessions Name Value ---- ----- ubuntu64esxi Renci.SshNet.SshClient 192.168.1.153 Renci.SshNet.SshClient PS E:\> New-SshSession -ComputerName 192.168.1.1 -Username root No key provided. Enter SSH password for root: ***************** Successfully connected to 192.168.1.1 PS E:\> $SshSessions.Keys ubuntu64esxi 192.168.1.1 192.168.1.153
Invoke-SshCommand
Invoke-SshCommand Help Text
<# .SYNOPSIS Invoke/run commands via SSH on target hosts for which you have already opened connections using New-SshSession. See Get-Help New-SshSession. .DESCRIPTION Execute/run/invoke commands via SSH.You are already authenticated and simply specify the target(s) and the command.
Output is emitted to the pipeline, so you collect results by using: $Result = Invoke-SshCommand [...] $Result there would be either a System.String if you target a single host or a System.Array containing strings if you target multiple hosts. If you do not specify -Quiet, you will also get colored Write-Host output - mostly for the sake of displaying progress. Use -InvokeOnAll to invoke on all computers to which you have opened connections. The hosts will be processed in alphabetically sorted order. .PARAMETER ComputerName Target hosts to invoke command on. .PARAMETER Command Required. The Linux command to run on specified target computers. .PARAMETER Quiet Causes no colored output to be written by Write-Host. If you assign results to a variable, no progress indication will be shown. .PARAMETER InvokeOnAll Invoke the specified command on all computers for which you have an open connection. Overrides -ComputerName, but you will be asked politely if you want to continue, if you specify both parameters. #>
Invoke-SshCommand Example
PS E:\temp> $Results = Invoke-SshCommand -InvokeOnAll -Command 'uname -a' ubuntu64esxi: Linux ubuntu64esxi 2.6.32-40-generic #87-Ubuntu SMP Tue Mar 6 00:56:56 UTC 2012 x86_64 GNU/Linux 192.168.1.1: Linux linksys 2.4.20 #1 Sun Nov 29 06:53:09 PST 2009 mips GNU/Linux 192.168.1.153: Linux localhost.localdomain 2.6.32-220.7.1.el6.x86_64 #1 SMP Wed Mar 7 00:52:02 GMT 2012 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux PS E:\temp> $Results Linux ubuntu64esxi 2.6.32-40-generic #87-Ubuntu SMP Tue Mar 6 00:56:56 UTC 2012 x86_64 GNU/Linux Linux linksys 2.4.20 #1 Sun Nov 29 06:53:09 PST 2009 mips GNU/Linux Linux localhost.localdomain 2.6.32-220.7.1.el6.x86_64 #1 SMP Wed Mar 7 00:52:02 GMT 2012 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
You might find yourself wanting to do something not supported by the module. You can run a command like this:
PS E:\> $SshSessions.'debian64esxi'.RunCommand('pwd')
CommandText : pwd
CommandTimeout : -00:00:00.0010000
ExitStatus : 0
OutputStream : Renci.SshNet.Common.PipeStream
ExtendedOutputStream : Renci.SshNet.Common.PipeStream
Result : /home/joakimbs
Error :
PS E:\> $SshSessions.'debian64esxi'.RunCommand('pwd').Result
/home/joakimbs
# Remove the trailing newline/whitespace (and any leading whitespace if it's there)
PS E:\> $SshSessions.'debian64esxi'.RunCommand('pwd').Result.Trim()
/home/joakimbs
PS E:\>
Most of the technicalities are taken care of for you if you use the pre-made Invoke-SshCommand, but I figure it might be useful to know this. Before output is returned by Invoke-SshCommand, any trailing carriage returns and newlines are removed from the output before it's sent to the pipeline.
Get-SshSession
Get-SshSession lists all connections you've created with New-SshSession. They will be listed alphabetically. The function can be piped to Format-Table -AutoSize for a more condensed representation on the console (some other stuff too, but not in this case, I would think).
You can specify the optional parameter -ComputerName. If you specify a host for which there is no key in the hash, you will get back the string "NULL" as the value for the "Connected" column.Get-SshSession Help Text
<# .SYNOPSIS Shows all, or the specified, SSH sessions in the global $SshSessions variable, along with the connection status. .DESCRIPTION It checks if they're still reported as connected and reports that too. However, they can have a status of "connected" even if the remote computer has rebooted. Seems like an issue with the SSH.NET library and how it maintains this status. If you specify hosts with -ComputerName, which don't exist in the $SshSessions variable, the "Connected" value will be "NULL" for these hosts. Also be aware that with the version of the SSH.NET library at the time of writing, the host will be reported as connected even if you use the .Disconnect() method on it. When you invoke the .Dispose() method, it does report the connection status as false. .PARAMETER ComputerName Optional. The default behavior is to list all hosts alphabetically, but this lets you specify hosts to target specifically. NULL is returned as the connection status if a non-existing host name/IP is passed in. #>
Get-SshSession Example
PS E:\> Get-SshSession | ft -auto ComputerName Connected ------------ --------- 192.168.1.1 True 192.168.1.153 True debian64esxi True ubuntu64esxi True
To store all the hosts, sorted alphabetically by Get-SshSession, in an array, do something like this (by the way, it's important not to use Format-Table in this one-liner...):
PS E:\> $Hosts = Get-SshSession | select -ExpandProperty ComputerName PS E:\> $Hosts 192.168.1.1 192.168.1.153 debian64esxi ubuntu64esxi PS E:\> $Hosts.Count 4
Enter-SshSession
Enter-SshSession Help Text
<# .SYNOPSIS Enter a primitive "interactive" SSH session against a target host. Commands are executed on the remote host as you type them and you are presented with a Linux-like prompt. .DESCRIPTION Enter commands that will be executed by the host you specify and have already opened a connection to with New-SshSession.You can not change the current working directory on the remote host.
.PARAMETER ComputerName Required. Target host to connect with. .PARAMETER NoPwd Optional. Do not try to include the default remote working directory in the prompt. #>
Enter-SshSession Example
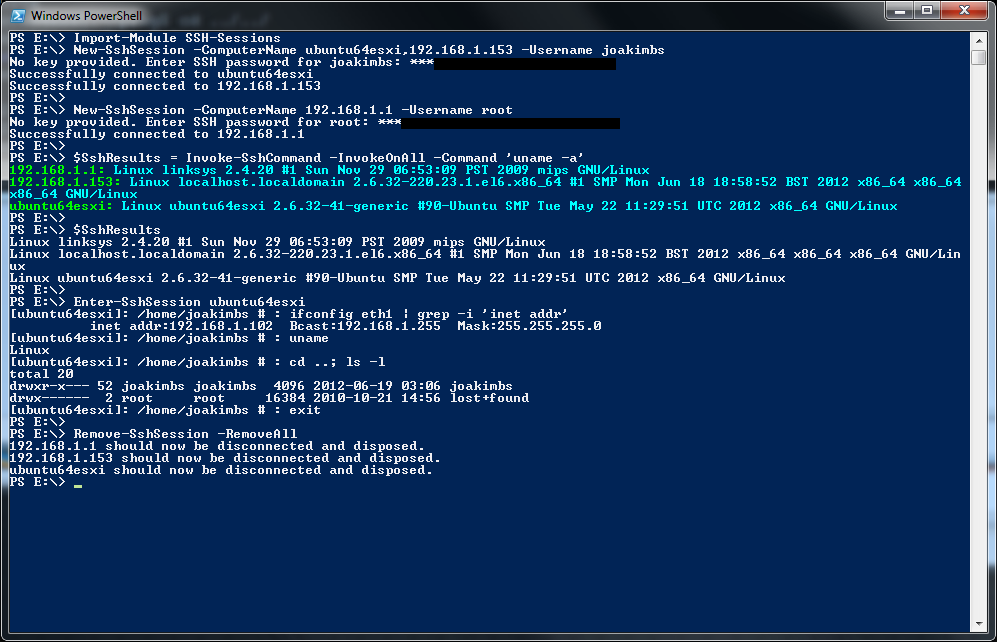
PS E:\temp> Enter-SshSession -ComputerName ubuntu64esxi
[ubuntu64esxi]: /home/joakimbs # : ifconfig eth1
eth1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:0d:29:24:07:c9
inet addr:192.168.1.102 Bcast:192.168.1.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::20c:29ff:fe25:7d9/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:184107 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:29856 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:47733722 (47.7 MB) TX bytes:4641823 (4.6 MB)
[ubuntu64esxi]: /home/joakimbs # : uname -a
Linux ubuntu64esxi 2.6.32-40-generic #87-Ubuntu SMP Tue Mar 6 00:56:56 UTC 2012 x86_64 GNU/Linux
[ubuntu64esxi]: /home/joakimbs # : cd ..; ls -l
total 20
drwxr-xr-x 51 joakimbs joakimbs 4096 2012-04-18 04:42 joakimbs
drwx------ 2 root root 16384 2010-10-21 14:56 lost+found
[ubuntu64esxi]: /home/joakimbs # : exit
PS E:\temp>
Remove-SshSession
Remove-SshSession Help Text
<# .SYNOPSIS Removes opened SSH connections. Use the parameter -RemoveAll to remove all connections. .DESCRIPTION Performs disconnect (if connected) and dispose on the SSH client object, then sets the $global:SshSessions hashtable value to $null and then removes it from the hashtable. .PARAMETER ComputerName The names of the computers for which you want to remove connections. .PARAMETER RemoveAll Removes all open connections and effectively empties the hash table. Overrides -ComputerName, but you will be asked politely if you are sure, if you specify both. #>
Remove-SshSession Example
PS E:\temp> Remove-SshSession -RemoveAll ubuntu64esxi should now be disconnected and disposed. 192.168.1.1 should now be disconnected and disposed. 192.168.1.153 should now be disconnected and disposed. PS E:\temp>
SCP Add-on Feature
Note made 2022-01-11: I made a couple of thousand dollars from this, but have not had a sale in probably 5 years. The reason is that you can find free, open-source alternatives now. Using the open-source WinSCP dll is also a good option. :)
Experimental sudo Support
This screenshot demonstrates running a sudo command from PowerShell against Ubuntu 16.04 (test performed 2017-02-25). On 2017-03-27 I tested that it works identically on CentOS7.
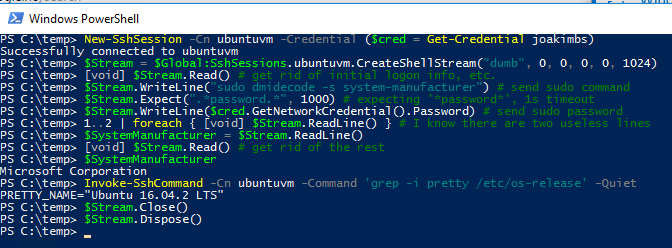
As text for copying, etc.:
New-SshSession -Cn 192.168.1.6 -Credential $Cred
Successfully connected to 192.168.1.6
$Stream = $Global:SshSessions."192.168.1.6".CreateShellStream("dumb", 0, 0, 0, 0, 1024)
[void] $Stream.Read() # get rid of initial logon into, etc. if any
$Stream.WriteLine("sudo dmidecode -s system-manufacturer") # send sudo command
$Stream.WriteLine($cred.GetNetworkCredential().Password) # send sudo password
1..2 | foreach { [void] $Stream.ReadLine() } # I found these two lines aren't needed
$SystemManufacturer = $Stream.ReadLine()
[void] $Stream.Read() # get rid of the rest
$SystemManufacturer
Microsoft Corporation
Invoke-SshCommand -Cn 192.168.1.6 -Quiet -Command 'grep -i pretty /etc/os-release'
PRETTY_NAME="CentOS Linux 7 (Core)"
$Stream.Close()
$Stream.Dispose()
Downloads
On 2016-11-05 I updated to the 2016.0.0 SSH.NET DLL, which has now moved to GitHub. You might want to ensure that you have the latest version by visiting the SSH.NET project page and checking the downloads. The module using the .NET 3.5 DLL expects it to have the name Renci.SshNet35.dll - and the .NET 4.0 version expects Renci.SshNet.dll. The .NET 4.0 version should work with PSv3, version 4 and 5. Doing my solemn duty and updating here.
The version in the PowerShell gallery and the PSv3 and up version (see below), v1.6+, has been rewritten a bit and now has a -Credential parameter as well as -KeyPass and -KeyCredential parameters. Before I updated to the latest DLL, I got this error when connecting to an Ubuntu 16.04 computer: Unable to connect to ubuntuvm: Exception calling "Connect" with "0" argument(s): "An established connection was aborted by the software in your host machine." *SSH-Sessions.zip - .NET 3.5 / PowerShell v2-compatible (legacy version - differs from the PowerShell gallery and GitHub version). *SSH-SessionsPSv3.zip - .NET 4.0 / PowerShell v3 and later. Now the same as the version in the PowerShell gallery and on GitHub as of 2017-11-11.Latest version in the wiki (not maintained for years, please use the versions in the PowerShell gallery, the older ones before 2.x.x are compatible with PowerShell version 2):
*SSH-Sessions.zip *
SSH-SessionsPSv3.zip
The PowerShell gallery version
If you have Windows Management Framework 5 or higher (WMF 5 is available for Windows 7 and up), you can install my SSHSessions module from the PowerShell gallery, a Microsoft site and online repository for scripts.
I had to change the name to "SSHSessions" in the PowerShell gallery since someone else had previously used "SSH-Sessions" (initially published to the gallery on 2017-01-26).To install with WMF 5 and up (to get the latest SSHSessions module version available), simply run this command (requires an internet connection):
Install-Module -Name SSHSessions
To install for your user only:
Install-Module -Name SSHSessions -Scope CurrentUser # no admin required
An attempt at a version history in the wiki (this is for the version in the PS gallery):
Adopting semantic versioning as of 2019-06-04. *2018-02-20: v2.1.1. Fix bug that caused calling scripts to terminate and raise a script-level exception when Get-SshSession had no sessions and also when Remove-SshSession -RemoveAll was called. Updated on GitHub and in the PowerShell gallery on 2018-02-18.*2018-01-01: v2.1. Standardize to use Write-Verbose, Write-Warning and Write-Error. Quiet on success, without -Verbose. Another possibly breaking change if New-SshSession output is parsed, etc. Use an old module version if needed. v1.7.1 should be compatible with all "old meta scripts" you might find on the internet, plus the PSv2 version.
*2018-01-01: v2.0. Major, breaking changes. Return objects instead of strings and a boolean (true/false) "Error" property value.
*2017-11-11: v1.9. Add a handy -Reconnect parameter to New-SshSession. Possibly breaking change if you currently parse feedback/output: It's now standardized to Ansible style consistently.
*2017-09-03: v1.8. Ansible style on non-quiet output. Pipeline support almost everywhere (except where it would break stuff - that I could think of).
*2017-08-17: v1.7.1. Made it so you can omit -KeyPass, so it works with keys with no password (maybe sending in a blank one works too). Based on feedback.
*2017-02-07: v1.7. Corrected a bug where "PlainTextPassword" was hard-coded into the script instead of the variable $Password that was supposed to be there. Pushed version 1.7 to the gallery. This bug does not / did not exist in the version in the wiki (but that doesn't have the -Credential parameter or key password/credentials parameters).
Please let me know about obvious bugs in the module itself! svendsentech@gmail.com or use GitHub.
The PowerShell gallery version is now also on GitHub here.
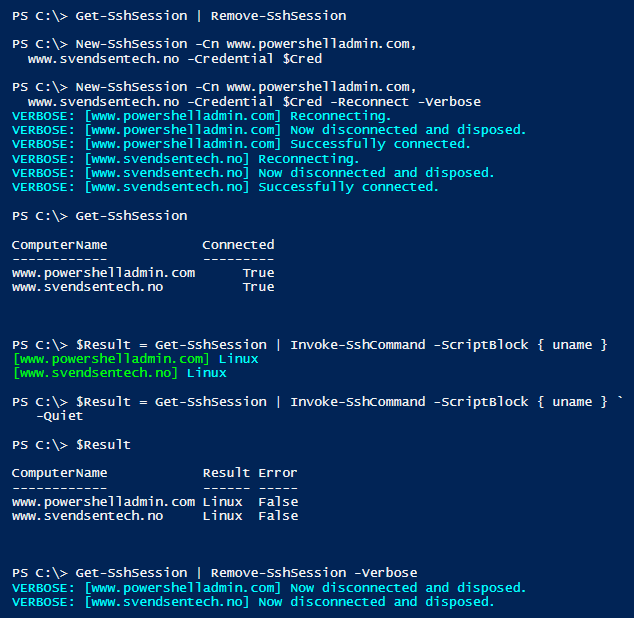
Demo of pipeline support
PS C:\> Get-SshSession
ComputerName Connected
------------ ---------
www.powershelladmin.com True
www.svendsentech.no True
PS C:\> Get-SshSession | Remove-SshSession
[www.powershelladmin.com] Now disconnected and disposed.
[www.svendsentech.no] Now disconnected and disposed.
PS C:\> New-SshSession -Cn www.powershelladmin.com,
www.svendsentech.no -Credential $Cred
[www.powershelladmin.com] Successfully connected.
[www.svendsentech.no] Successfully connected.
PS C:\> $Result = Get-SshSession | Invoke-SshCommand `
-ScriptBlock { uname }
[www.powershelladmin.com] Linux
[www.svendsentech.no] Linux
PS C:\> $Result
ComputerName Result Error
------------ ------ -----
www.powershelladmin.com Linux False
www.svendsentech.no Linux False
Screenshot of the same:

A Few Quick Tips About How To Use The Module
PS E:\> $env:PSModulePath -split ';' C:\Users\joakim\Documents\WindowsPowerShell\Modules C:\Windows\system32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\Modules\
If the folders do not exist, you need to create them. So to use this SSH-Sessions module, unzip the files into a folder called SSH-Sessions inside one of the module folders (Microsoft says "never put anything in the modules folder in C:\Windows, because it's ours", but...). The full path in my case is '''C:\Users\joakim\Documents\WindowsPowerShell\Modules\SSH-Sessions''' (this is for my profile/user only).
Then you use the cmdlet ''Import-Module'' to load the module after it's copied to the proper path:Note made 2022-01-11: Now that the world has PowerShell version 5.1 and PowerShell Core/7, we have a $Env:ProgramFiles\WindowsPowerShell\Modules for machine-wide modules (requires administrator permissions to write there by default). I believe it was introduced with Windows Management Framework 4 (default in Server 2012).
PS E:\> Import-Module SSH-Sessions PS E:\>
To load the module automatically when you start PowerShell, put this Import-Module command in your PowerShell profile (external Microsoft Technet site link).
From PowerShell version 3 and on, modules are auto-loaded when you type the name of a cmdlet/parameter in a module (nice feature!).You can also use Import-Module on the (relative) path to the module, like so:
PS E:\> Import-Module .\MyPSModules\SSH-Sessions
A Few Notes About Creating a Key for ESXi 5.x
*Download puttygen.exe, open it and click Generate to generate a private/public key pair. I set the number of key bits to 4096. This could still be a bit high as of 2022, but it's proactive - unless it matters for performance in your case?
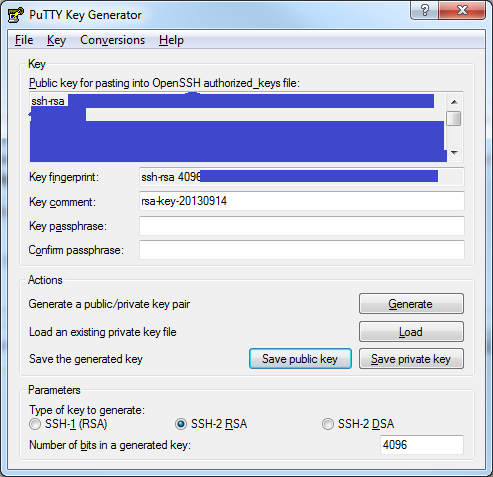 *Then export the private key for use with the SSH-Sessions module (has to be in OpenSSH format - the Putty key format will not work as of 2013-09-14).
**Use the menu choice Conversions -> Export OpenSSH Key.
*Then export the private key for use with the SSH-Sessions module (has to be in OpenSSH format - the Putty key format will not work as of 2013-09-14).
**Use the menu choice Conversions -> Export OpenSSH Key.*Place the contents of the top field (the public key) in /etc/ssh/root-keys/authorized_keys on the ESXi target, for instance like this (see this VMware article for more information).
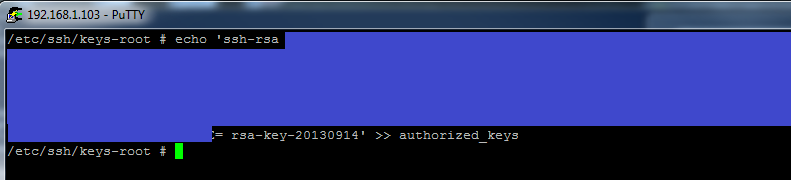
Note made 2022-01-11: I now know the public key did not have to be hidden. :D
# echo 'YOUR KEY HERE' >> /etc/ssh/keys-root/authorized_keys
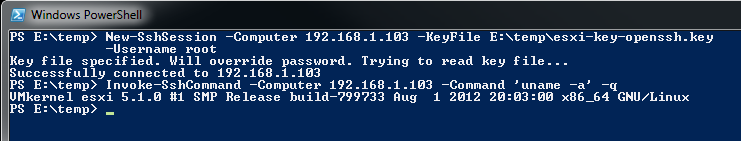
Then connect specifying the key you exported from puttygen.exe earlier:
PS E:\temp> New-SshSession -Computer 192.168.1.103 -KeyFile E:\temp\esxi-key-openssh.key
-Username root
Key file specified. Will override password. Trying to read key file...
Successfully connected to 192.168.1.103
PS E:\temp> Invoke-SshCommand -Computer 192.168.1.103 -Command 'uname -a' -q
VMkernel esxi 5.1.0 #1 SMP Release build-799733 Aug 1 2012 20:03:00 x86_64 GNU/Linux
PS E:\temp>
Blog articles in alphabetical order
A
- A Look at the KLP AksjeNorden Index Mutual Fund
- A primitive hex version of the seq gnu utility, written in perl
- Accessing the Bing Search API v5 using PowerShell
- Accessing the Google Custom Search API using PowerShell
- Active directory password expiration notification
- Aksje-, fonds- og ETF-utbytterapportgenerator for Nordnet-transaksjonslogg
- Ascii art characters powershell script
- Automatically delete old IIS logs with PowerShell
C
- Calculate and enumerate subnets with PSipcalc
- Calculate the trend for financial products based on close rates
- Check for open TCP ports using PowerShell
- Check if an AD user exists with Get-ADUser
- Check when servers were last patched with Windows Update via COM or WSUS
- Compiling or packaging an executable from perl code on windows
- Convert between Windows and Unix epoch with Python and Perl
- Convert file encoding using linux and iconv
- Convert from most encodings to utf8 with powershell
- ConvertTo-Json for PowerShell version 2
- Create cryptographically secure and pseudorandom data with PowerShell
- Crypto is here - and it is not going away
- Crypto logo analysis ftw
D
G
- Get rid of Psychology in the Stock Markets
- Get Folder Size with PowerShell, Blazingly Fast
- Get Linux disk space report in PowerShell
- Get-Weather cmdlet for PowerShell, using the OpenWeatherMap API
- Get-wmiobject wrapper
- Getting computer information using powershell
- Getting computer models in a domain using Powershell
- Getting computer names from AD using Powershell
- Getting usernames from active directory with powershell
- Gnu seq on steroids with hex support and descending ranges
- Gullpriser hos Gullbanken mot spotprisen til gull
H
- Have PowerShell trigger an action when CPU or memory usage reaches certain values
- Historical view of the SnP 500 Index since 1927, when corona is rampant in mid-March 2020
- How Many Bitcoins (BTC) Are Lost
- How many people own 1 full BTC
- How to check perl module version
- How to list all AD computer object properties
- Hva det innebærer at særkravet for lån til sekundærbolig bortfaller
I
L
M
P
- Parse openssl certificate date output into .NET DateTime objects
- Parse PsLoggedOn.exe Output with PowerShell
- Parse schtasks.exe Output with PowerShell
- Perl on windows
- Port scan subnets with PSnmap for PowerShell
- PowerShell Relative Strength Index (RSI) Calculator
- PowerShell .NET regex to validate IPv6 address (RFC-compliant)
- PowerShell benchmarking module built around Measure-Command
- Powershell change the wmi timeout value
- PowerShell check if file exists
- Powershell check if folder exists
- PowerShell Cmdlet for Splitting an Array
- PowerShell Executables File System Locations
- PowerShell foreach loops and ForEach-Object
- PowerShell Get-MountPointData Cmdlet
- PowerShell Java Auto-Update Script
- Powershell multi-line comments
- Powershell prompt for password convert securestring to plain text
- Powershell psexec wrapper
- PowerShell regex to accurately match IPv4 address (0-255 only)
- Powershell regular expressions
- Powershell split operator
- Powershell vs perl at text processing
- PS2CMD - embed PowerShell code in a batch file
R
- Recursively Remove Empty Folders, using PowerShell
- Remote control mom via PowerShell and TeamViewer
- Remove empty elements from an array in PowerShell
- Remove first or last n characters from a string in PowerShell
- Rename unix utility - windows port
- Renaming files using PowerShell
- Running perl one-liners and scripts from powershell
S
- Sammenlign gullpriser og sølvpriser hos norske forhandlere av edelmetall
- Self-contained batch file with perl code
- Silver - The Underrated Investment
- Simple Morningstar Fund Report Script
- Sølv - den undervurderte investeringen
- Sort a list of computers by domain first and then name, using PowerShell
- Sort strings with numbers more humanely in PowerShell
- Sorting in ascending and descending order simultaneously in PowerShell
- Spar en slant med en optimalisert kredittkortportefølje
- Spre finansiell risiko på en skattesmart måte med flere Aksjesparekontoer
- SSH from PowerShell using the SSH.NET library
- SSH-Sessions Add-on with SCP SFTP Support
- Static Mutual Fund Portfolio the Last 2 Years Up 43 Percent
- STOXR - Currency Conversion Software - Open Exchange Rates API
